INTERNAL GRAVITY WAVE PROPAGATION
: ILLUSTRATE VARIOUS FEATURES OF WAVE MOTION AND TURBULENCE IN A STATICALLY
STABLE SALT STRATIFICATION
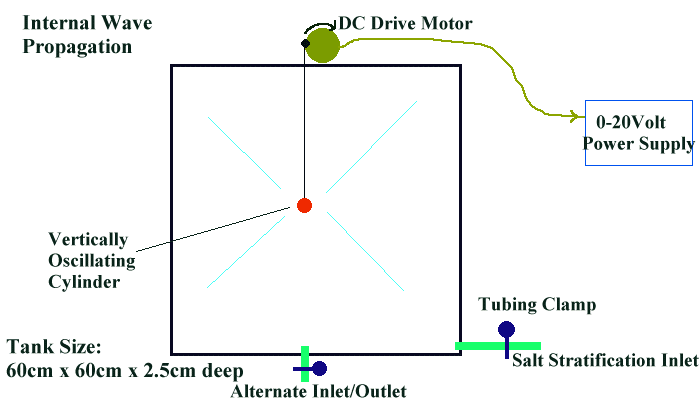
- Create a salt stratification in a tall shallow box (see salt
stratification maker). Use 20% (strong) salt solution in the salt
chamber.
- Fill slowly, letting fresh in first. Cylinder should be in position
while filling.
- Wait for stratification to smooth out (overnight).
- Wheel into class. Be careful not to bumb stratification too much.
- Attach drive motor to power supply.
- Visualization is by shadowgraph. Shine projector through the flat
side of the tank then onto a wall. The white light projector uses a
box slide to crop the beam. Position the projector as far away from
the tank as possible (i.e. make it like a point source). The tank
should be far enough away from a white wall to permit students to see both
the tank and the image on the wall.
- Start with a slow small amplitude oscillation. Compare beam angle
with prediction. Change frequency, not change in beam angle.
- Drag cylinder horizontally to see lee wave formation or blocking.
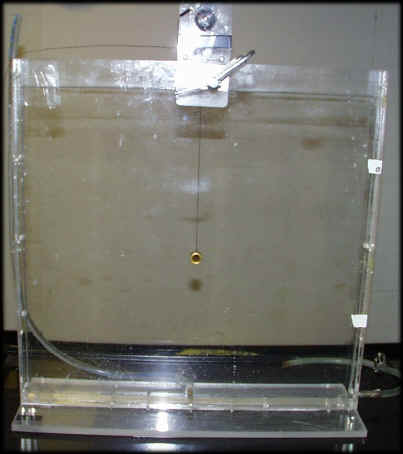

Tank with drive motor and cylinder at mid depth.

Close up of drive motor. Hook suspension string closest to axis for
weak waves. Also, high frequency up down motion will generate turbulence
and collapse near the cylinder.

Drive motor power supply. Start with a low voltage (low frequency)
oscillation.
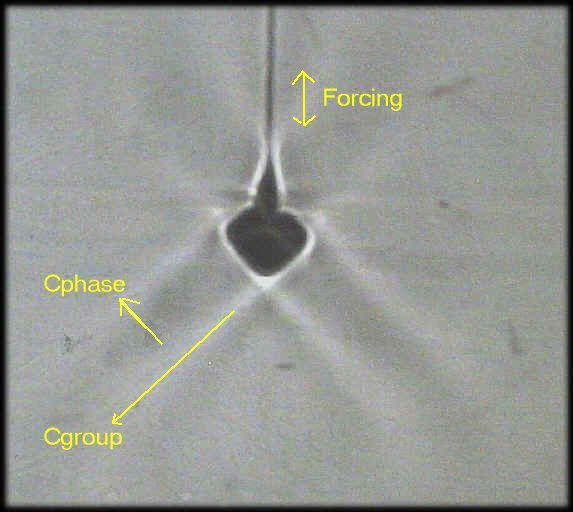
Picture of the beaming.
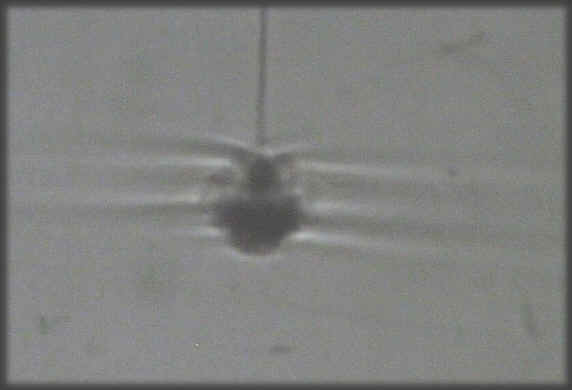
Picture of trapping, when forcing frequency is higher than Brunt Vaisala
frequency ( root (g*delrho/rho*H)).
MOVIES:
- QUASI LINEAR
WAVE PROPAGATION
- TOWING THROUGH
A STRATIFIED FLUID: LEE WAVES - (FOLLOWED BY INADVERTENT RISE OF
OBSTACLE AND COLLAPSE OF STRATIFICATION INTO A LAYERED SYSTEM
(BIG SCREEN)
SALT STRATIFICATION GENERATOR
©2000.
John Hart, University of Colorado






